You might have heard about the %LocalAppData% folder, but you still do not know what it is for, or how you can access it. In this guide, you will learn everything about what is LocalAppData folder and how to access it on Windows system. But first, you should be conscious that this folder is hidden by default because it contains data and information that should not be deleted or modified. That is why it is always a good idea to avoid making any changes to LocalAppData as much as possible to keep your system in good condition.
What is LocalAppData on Windows Used for?
Available in old operating systems like Windows Vista, 7, 8, and now even on Windows 10 and Windows 11, the LocalAppData folder stores data and settings for applications and programs that is available on your PC. All the documents the same folder has are very important for the smooth running of the system and the programs you have installed on your PC. Each Windows user account contains its own LocalAppData folder, so if you have several user accounts on your computer, you will also have multiple AppData folders.
How to Access LocalAppData on Windows
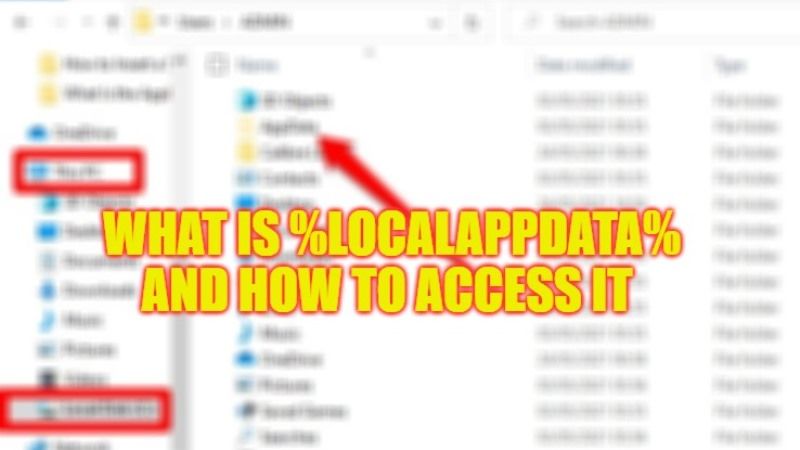
- First, you need to open File Explorer, so you can click on its icon on the Windows Taskbar or by pressing the Windows + E keys keyboard shortcut.
- Now, if you want to see hidden folders like AppData, click the View tab in the Explorer window on the top, then tick mark the Hidden Items box in the Show/Hide section.
- In the left side pane, click “This PC”.
- Then click on your primary drive, which will be the (C:) drive.
- On the right side, click on the Users folder.
- After that click on your main user account folder, for example – C:\Users\(username).
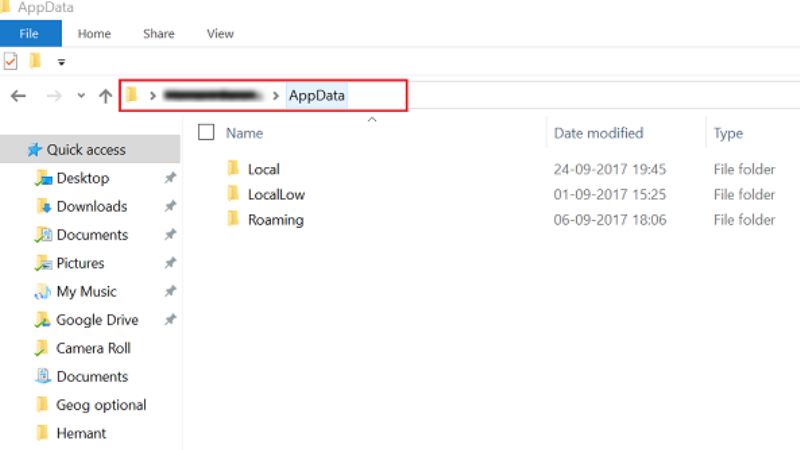
- Finally, click on the AppData folder. Here you will find three folders: Local (which is the %LocalAppData%), LocalLow, and Roaming.
That is everything you need to know about what is LocalAppData folder and how to access it on the Windows operating system. While you are here, you might be also interested to know What is SFC Scannow and How to Use This Command on Windows, and What Is Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Virtual Adapter.